- Hypoimmune-modified allogeneic iPSCs evade immune response and rejection without immunosuppression in non-human primate model
- Long-term survival and immune evasion of hypoimmune-modified allogeneic iPSCs at least equivalent to survival of autologous iPSCs
- CD47 overexpression provided robust protection of hypoimmune-modified allogeneic cells from killing by the innate immune system versus other engineering approaches
Sana Biotechnology, a company focused on changing the possible for patients through engineered cells, today announced that Nature Biotechnology has published a paper titled “Hypoimmune induced pluripotent stem cells survive long term in fully immunocompetent, allogeneic rhesus macaques.” The preclinical studies published in this paper used Sana’s hypoimmune (HIP) technology to engineer HIP-modified allogeneic cells to escape immune detection in the absence of immune suppression. In vivo studies in fully immunocompetent non-human primates (NHPs) demonstrated that HIP-modified allogeneic cells survived without immunosuppression for the length of the studies (16 weeks and >40 weeks). An additional humanized mouse study showed that HIP-modified induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) that are differentiated into pancreatic islet cells were immune evasive and ameliorated diabetes in vivo.
“We have demonstrated in numerous preclinical studies that our hypoimmune-engineered cells persist and function without eliciting an immune response,” said Doug Williams, PhD, Sana’s President of Research and Development. “These published data in rigorous translational models that closely imitate the human immune system support our previous findings, most importantly that HIP-modified allogeneic cells avoid immune recognition and rejection without immune suppression. We are incorporating the HIP technology into multiple therapeutic candidates in our pipeline and look forward to reporting our first human clinical data later this year.”
Allogeneic HIP Cells Avoid Immune Activation and Escape Systemic Immune Rejection in NHPs
NHP iPSCs were engineered using HIP technology to generate HIP-modified iPSCs. A cross-over study was performed where NHP HIP iPSCs (HIPallo) were administered to NHPs previously sensitized to non-engineered NHP iPSCs (wtallo) and wtallo cells were administered to NHPs previously transplanted with HIPallo cells. In NHPs first receiving HIPallo cells, no cellular immune activation or killing of HIPallo cells was observed after cell transplantation. Subsequent injection of wtallo cells into these NHPs induced strong cellular immune responses similar to those observed in the group receiving wtallo cells first. The HIPallo cells survived with no evidence of immune recognition despite this immune response to wtallo cells. In contrast, NHPs initially transplanted with wtallo cells showed rapid immune sensitization, including strong T cell activation and killing of the wtallo cells. Subsequent transplantation of HIPallo cells showed survival and no cellular immune response to HIPallo cells despite the previous immune activation to and killing of wtallo cells.
In all instances, administration of HIPallo cells did not generate de-novo antibodies and no antibody-related killing of HIPallo cells was observed, regardless of the order of administration. In contrast, administration of wtallo cells provoked a vigorous antibody and killing response against these cells.
In a separate study using human iPSCs, hypoimmune-modified human iPSCs (HIPxeno iPSCs) and unmodified human iPSCs (wtxeno iPSCs) were transplanted into NHPs. Similar results were observed and demonstrated the ability of HIPxeno iPSCs to avoid immune activation and recognition, whereas wtxeno iPSCs induced a strong immune response.
Human HIP iPSCs Differentiated into All Three Germ Layers, Collectively Avoiding Immune Recognition; HIP Primary Islet Cells Survive for Over 40 Weeks in NHP
In the allogeneic setting following transplantation into the NHP, iPSCs differentiated in vivo and gave rise to cells from all three germs layers (endoderm, medoderm, and ectoderm). These HIP-modified cells avoided immune recognition, survived, and engrafted in immunocompetent NHPs, supporting the notion that cells remain hypoimmune through differentiation and that the various HIP derivatives are protected from immune recognition even after differentiation.
In another study, HIP-modified allogeneic primary islet cells achieved long-term survival after transplantation for over 40 weeks and evaded immune recognition without the use of immunosuppression in one NHP. An additional study in immunocompetent allogeneic humanized mice demonstrated that human HIP iPSC-derived islet cells are functional and ameliorated diabetes following transplantation.
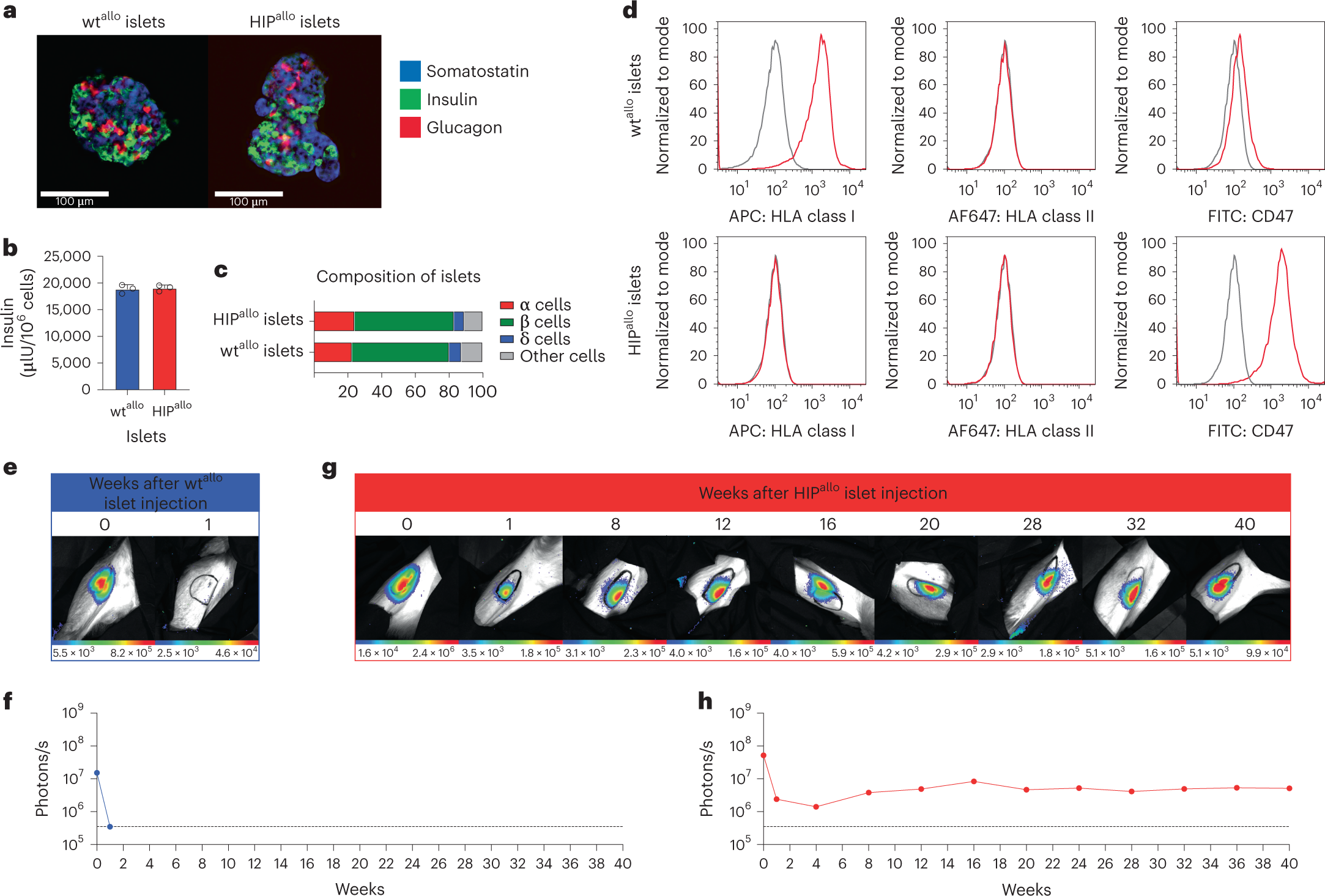
Allogeneic HIP islets achieve long-term survival
a, Immunofluorescence pictures of dissociated and reaggregated wtallo and HIPallo islets from rhesus monkeys (representative images). b, In vitro insulin secretion of wtallo and HIPallo islets (mean ± s.d., triplicates). c, The composition of wtallo and HIPallo islets of α, β, δ and other cells (mean, triplicates). d, Flow cytometry histograms for HLA class I and II and rhesus CD47 on wtallo and HIPallo islets (representative images). e–h, The survival of FLuc+ wtallo and HIPallo islets in allogeneic rhesus monkeys was followed by BLI (one animal each).
Only Transgenic CD47 Overexpression Provided Widespread Protection Against the Innate Immune Response
The depletion of class I and II human leukocyte antigens (HLA) is an engineering strategy aimed at broadly avoiding recognition by the adaptive immune system. This depletion, however, triggers recognition by the innate system, including a killing response by NK cells and macrophages. Head-to-head comparisons of strategies to counteract this response were conducted and data showed that strategies using HLA-E, HLA-G, or PD-L1 did not prevent innate immune recognition. Only CD47 overexpression prevented both adaptive and innate immune recognition in vitro and in vivo.
About Sana’s Hypoimmune Platform
Sana’s hypoimmune platform is designed to create cells ex vivo that can “hide” from the patient’s immune system to enable the transplant of allogeneic cells without the need for immunosuppression. We are applying hypoimmune technology to both donor-derived allogeneic T cells, with the goal of making potent and persistent CAR T cells at scale, and pluripotent stem cells, which can then be differentiated into multiple cell types at scale. Preclinical data from a variety of cell types demonstrate that these transplanted allogeneic cells can evade both the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system while retaining their function. Our most advanced programs using hypoimmune technology include our allogeneic CAR T program targeting CD19+ cancers, our allogeneic CAR T program targeting CD22+ cancers, our allogeneic CAR T program targeting BCMA+ cancers, and our stem-cell derived pancreatic islet cell program for patients with type 1 diabetes.
Source – Globe Newswire
Hu X, White K, Olroyd AG, DeJesus R, Dominguez AA, Dowdle WE, Friera AM, Young C, Wells F, Chu EY, Ito CE, Krishnapura H, Jain S, Ankala R, McGill TJ, Lin A, Egenberger K, Gagnon A, Michael Rukstalis J, Hogrebe NJ, Gattis C, Basco R, Millman JR, Kievit P, Davis MM, Lanier LL, Connolly AJ, Deuse T, Schrepfer S. (2023) Hypoimmune induced pluripotent stem cells survive long term in fully immunocompetent, allogeneic rhesus macaques Nat Biotechnol [Epub ahead of print]. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-01784-x